Production is an activity that adds value to a product. The aim is to organize production activities as rationally as possible. Depending on the nature of the product, its complexity, the quantity produced and the nomenclature, production is also organized differently.
On the basis of production volumes and nomenclature (number of different types of products), regularity of their production (how often the same type of product is re-produced) and stability (how long the same type of product is in production), three types of production are distinguished in mechanical engineering: single (individual), series (batch production) and mass production.
In the case of batch (piece) production, the production process usually takes place in different successive stages at different workplaces. Batch production, ie the discrete production of products, takes place either as individual production (a single unique product), serial production (batches of a certain size) or project production (organizational form for fulfilling orders in the company).
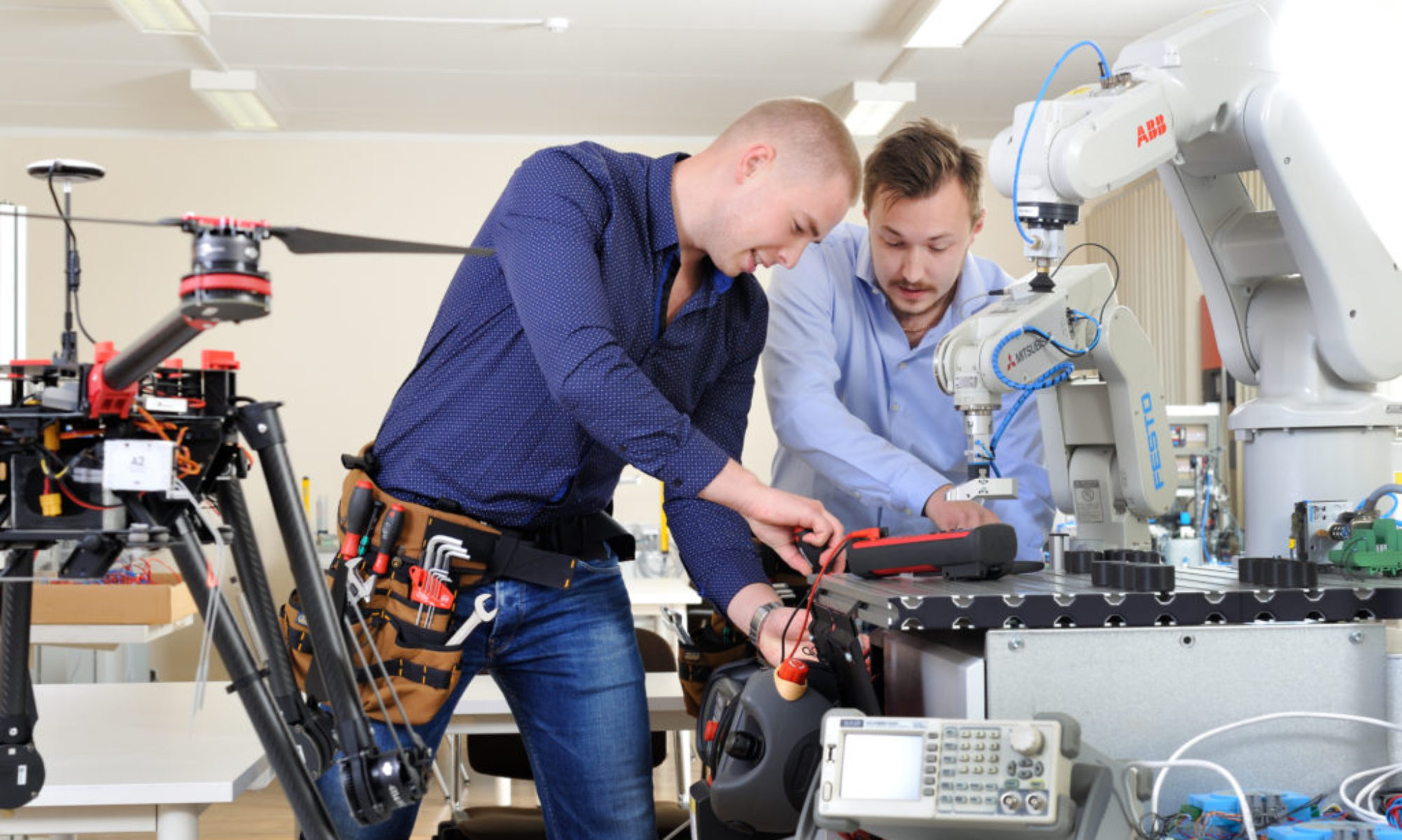
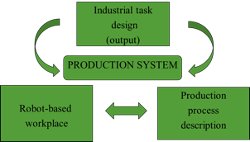
A production system is a complex system, where on the one hand there is a physical environment characterized by equipment and associated processing methods, and on the other hand there is an intellectual environment characterized by processes and people performing them to a greater or lesser extent (depending on the level of automation).
A workplace is a part of a production system and production process that performs specific technological tasks (performs processing operations) in accordance with the predetermined conditions given in the working drawing and work instructions. In addition, the operational technology and / or control technology may be described in more detail.
The workplace is a part of a production system / production department and its main function is to perform the given production task effectively, ie the quantity of the given products is produced in a timely and high-quality manner, using the available resources in the best possible way.
Certain tasks are planned for the workplace. These tasks are characterized by: product nomenclature, product characteristics, production volumes, product iterations, quality parameters.
Two workplaces are given as examples:
-
- robot welding workplace and
- machine tending workplace
A workplace must perform an industrial task:- According to the given technical parameters (drawing of a product)
-
- Following the rules (production technology) with
- High efficiency (KPI data) and
- with guaranteed quality.

Fig 2.1 Machine tending workplace

Fig 2.1 Robotized welding
References
[4] Richard K. Miller. Industrial Robot Handbook. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4684-6610-2
[5] Prof. Alessandro De Luca. Industrial Robotics. University of Roma. Department of Industrial Informatics and Automation
[6] Yoram Koren. Robotics for Engineers. McGraw Hill Book Company
Example of robotized assembly task description (E1)
The activity chosen for potential robotization is the installation and fastening of screws in the assembly process.
Assembly process
Currently there are 6 people working on an assembly line for products which require fastening with screws. Manual screwdrivers with controllable torque are currently used. The entire process is being completed manually by operators. The primary issues with operators are related to human-issues such as lost time due to illness and breaks, a high cost; and with the production quality as people tend to make mistakes as well as quality control is lower due to lack of factual quality control.
Currently the process consists of the five following steps on conveyor in the assembly workstation:
- Picking the housing from shelf and placing to the work area
- Picking PCB from shelf and placing to the work area
- Placing the PCB on housing
- Picking up screws
- Screwing the PCB onto the housing
After finishing these steps the assembly is being moved on the conveyor to the testing station.
After testing the finished product is sent on the conveyor to the packing station.
Nomenclature
Manufacturing is a mix of serial production and made-to-order production. As of today, the orders for the next month are as follows: TV-remotes, walkie-talkies and safety boxes. TV-remotes and walkie-talkies have orders for more than 20 000 products in total, safety boxes have an order of total 4000.
Amount
The mass production products are produced in high volumes - 24 000 pieces per month. The number of custom made products for clients is small - only one order with less than 5000 units per order.
Business model
As a sub-contractor the company is working based on the needs of the client. There are many clients who all want different products and therefore, the quantities and quality specifications vary greatly. There are clients who order for a longer period of time and also one-time orders. The manufacturing of the longer period orders can be called mass production where the products are standardized. One-time orders, however, are made-to-order and there are lots of different products produced in low volumes.
Integration
As the production is working on a conveyor line method, the integration of the robot is not needed with the rest of the machines except with the line itself. As the line is equipped already with sensors and stoppers to ensure no product is missed during the manufacturing then there would not be any problem about understanding whether the product is on the line or not. The integration with the robot could be easily integrated with the line if needed as the line is prepared to be connected with other systems.
Furthermore, there is an information sharing process set up to collect and store data received from production lines. The process has been set up with keeping in mind possible future additions to the system which allows to easily add the robot into the same data collection system with the rest of processes.
QUESTIONS Q2 / TASKS T2 – ROBOT-BASED MANUFACTURING DESCRIPTION
- Give an example of individual, batch and mass production
- What do you mean of value-added production
- Give a definition of a workplace. Give an example of a robot-based workplace
- What product data are important for determining the production process on a workplace
- Describe a task for manufacturing proceeding from a certain application area of robotization
- See application areas – Fig. 1.1
- See industrial task description example – (E1)
QUESTIONS Q2 / TASKS T2 – ROBOT-BASED MANUFACTURING DESCRIPTION
- Describe the integrated manufacturing
Integrated manufacturing pilt
- What kind of information is needed for production a workpiece in a workplace. From where the needed data would be obtained
- What are the needed information flows for robot-welding in a robot cell
- Describe a machine tending workplace
- Design a production task for robotization (see: Fig.1.1; (E1))

