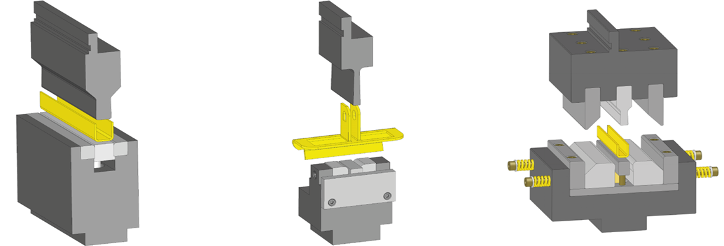
Basic

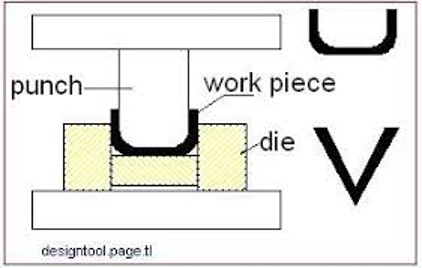
The press brake contains an upper tool called the punch and lower tool called the die between which the sheet metal is placed.
Bending is performed by a press brake machine that can be automatically or manually loaded. Press brakes are available in a variety of different sizes and lengths (20-200 tons) depending on the process requirements.
Bending is a process whereby a force is applied to sheet metal which causes it to bend at an angle and form the desired shape. Bends can be short or long depending on what the design requires. The sheet is placed between the two and held in place by the backstop. The bend angle is determined by the depth that the punch forces the sheet into the die. This depth is precisely controlled to achieve the required bend.
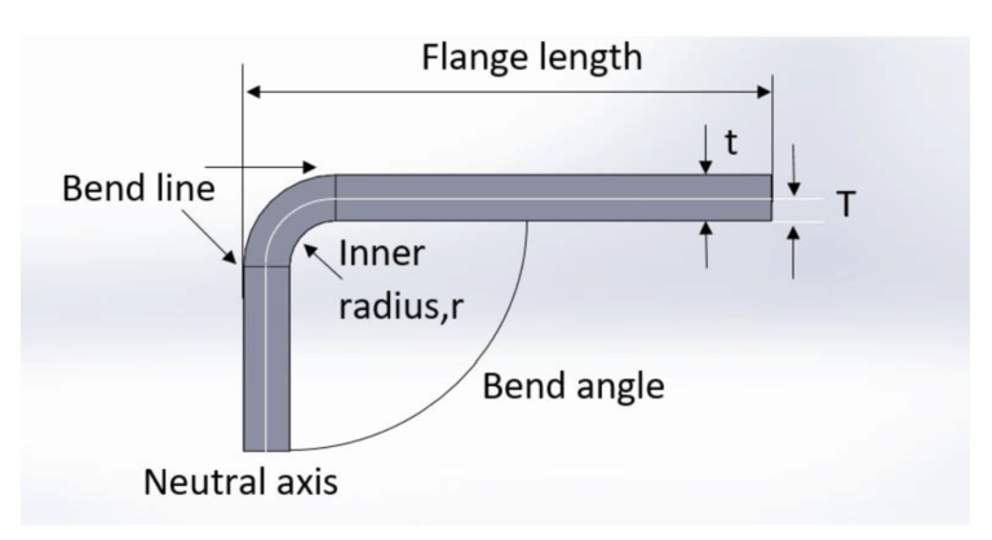
Bend line– The straight line on the surface of the sheet, on either side of the bend, that defines he end of the level flange and the start of the bend.
Bend radius – The distance from the bend axis to the inside surface of the material, between the bend lines.
Bend angle – The angle of the bend, measured between the bent flange and its original position, or as the included angle between perpendicular lines drawn from the bend lines. Sometimes specified as the inside bend radius. The outside bend radius is equal to the inside bend radius plus the sheet thickness.
Neutral axis – The location in the sheet that is neither stretched nor compressed, and therefore remains at a constant length.
K-factor – The location of the neutral axis in the material, calculated as the ratio of the distance of the neutral axis T, to the material thickness t. The K-factor is dependent upon several factors (material, bending operation, bend angle, etc.) and is greater than 0.25, but cannot exceed 0.50. K factor = T/t
Bend allowance – The length of the neutral axis between the bend lines or the arc length of the bend. The bend allowance added to the flange lengths is equal to the total flat length.
The K-factor is the ratio between the the neutral axis to the thickness of the material.

Importance of the K-factor in sheet metal design
The K-factor is used to calculate flat patterns because it is related to how much material is stretched during bending. Therefore it is important to have the value correct in CAD software. The value of the K-factor should range between 0 – 0,5. To be more exact the K-factor can be calculated taking the average of 3 samples from bent parts and plugging the measurements of bend allowance, bend angle, material thickness and inner radius into the following formula:
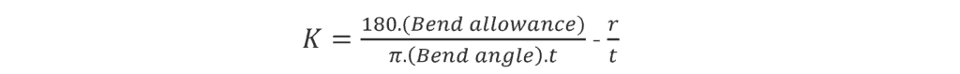
In sheet metal bending, a flat part is bent using a set of punches and dies. The punch and the die are mounted on a press-brake, which controls the relative motion between the punch and tie, and provides the necessary bending pressure.
Sheet metal bending process consists from the following stages:
- Position 1: part on the die
- Position 2: punch on the part
- Position 3: perform bending
- Position 4: take out the part
A press brake is a machine tool for bending sheet and plate material, most commonly sheet metal. It forms predetermined bends by clamping the workpiece between a matching punch and die.- Wikipedia
Bending process illustration: www.machinemfg.com
Press brake tools description
 |
Standard punches and dies
Standard punches and dies for press brake are required to perform the simple bends for the required degree according to the setup and the stroke of beam of the machine. The standard punches mean straight shape punches to make easy bends. The radius of the internal bend and the angle according to the geometry of the punch. Standard tools usually are the classic to perform the bending of boxes and simple shape parts with your press brak |
 |
Radius punches
If the internal radius is bigger than standard and should be obtained it is possible to use radius punches or radius inserts for punch holders with the desired radius to perform the large straight radius bending. Depends of the radius usually dies with big opening are used. Depends of the possibilities R=50 or even R=100 could be used. Press brakes with high tonnage are widely used for thick material profiles for heavy industries. |
 |
Gooseneck punches
To make the U-shape or channel straight punch probably can’t be used because of the collisions with the part and the metal of the punch. For this purposes usually gooseneck punches are used with the shape to have the possibility not to contact with the final flange of the part (radius internal shape). Gooseneck means the special execution of the punch to have the opening at the middle for the end of part. Variety of gooseneck punches could be very big from small till big dimensions. |
 |
Gooseneck special punches
For complicated profile shapes with closed geometry, special C-shape profiles etc. to perform the beds in U-shape and later – the last bend to close the profile, we are ready to develop and to offer special gooseneck punches according to the special geometry of your profileThese punches are manufactured according to the geometry of the profile, possibilities and stroke of your press brake during the bending to prevent any collisions and usually to make the job with one tool even if usually it takes several different punches. |
 |
Sharp bends punches and dies
To perform the sharp bends usually punches and dies with the 26-28-30 degrees are used (or knife punches). The reason for the requirements of sharp bends could be different but usually it is the pre-bend (first bend) of the part to be flattened after with side to the side. Prebending with such way could be the reason of minimal deformation during the future flattening. |
 |
Z-bend press brake tools
Special press brake tools (punch and die set or offset tools) could be used for special deformations with the way of stamping, for example Z-bend in one bend. To perform the bending of this way the geometry of the shape is usually used so the way of the deoformation is other than the air bending. The other stamping general job is to perform ribs on the sheetmetal with the use of press brake. |
Bending operation